Aluminum Siding Repair A Comprehensive Guide
Aluminum Siding Repair: This isn’t just about patching holes; it’s about restoring the curb appeal and protecting the integrity of your home’s exterior. We’ll delve into the common causes of damage – from the relentless assault of weather to accidental impacts – and explore the various repair techniques available. Whether you’re a seasoned DIY enthusiast or a homeowner facing an unexpected repair, this guide equips you with the knowledge and confidence to tackle the job, saving you time, money, and potential headaches down the road.
From identifying the type and severity of damage to selecting the right tools and materials, we’ll cover everything you need to know. We’ll even compare DIY repairs to professional services, helping you make the best decision for your situation. Think of this as your ultimate resource for transforming damaged aluminum siding into a gleaming, protective barrier for your home.
Understanding Aluminum Siding Damage
Aluminum siding, while durable, isn’t impervious to damage. Understanding the different types of damage and their causes is crucial for effective repair and, importantly, for preventing further deterioration. This knowledge empowers homeowners to make informed decisions about maintenance and repair, ultimately extending the lifespan of their siding.Aluminum siding damage can range from minor cosmetic blemishes to significant structural compromises.
Knowing the difference is key to prioritizing repairs and avoiding costly mistakes. Let’s delve into the specifics.
Types of Aluminum Siding Damage
The common types of damage to aluminum siding can be broadly categorized into dents, scratches, holes, and discoloration. Each type has its own set of causes and repair complexities. A systematic approach to assessing damage is vital for effective repair strategies.
| Damage Type | Cause | Severity | Repair Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dents | Impact from falling objects, sports equipment, or accidental collisions. | Varies; can be cosmetic or structural depending on depth and location. | For minor dents, gentle pushing from behind may suffice. Severe dents often require replacement panels. |
| Scratches | Abrasion from branches, landscaping tools, or furniture. | Generally cosmetic, but deep scratches can compromise the protective coating. | Minor scratches may be touched up with paint; deeper scratches might necessitate panel replacement. |
| Holes | Impact from projectiles, animal activity, or severe weather. | Significant structural damage, potentially leading to water ingress. | Repair involves patching or replacing the damaged section. Professional help is often recommended. |
| Discoloration | Exposure to UV radiation, environmental pollutants, or improper cleaning. | Primarily cosmetic, but severe fading can indicate underlying damage. | Cleaning and repainting can often restore the original appearance. Severe discoloration may require panel replacement. |
Factors Contributing to Aluminum Siding Deterioration
Several factors contribute to the degradation of aluminum siding over time. These factors often interact, accelerating the deterioration process. Understanding these factors allows for proactive maintenance and mitigation strategies.Weather plays a significant role. Prolonged exposure to sun, rain, snow, and extreme temperatures causes expansion and contraction, leading to stress fractures and eventual damage. For example, areas experiencing frequent freeze-thaw cycles often show accelerated deterioration.
Age is another key factor; the protective coatings on aluminum siding degrade over time, leaving the underlying metal vulnerable to corrosion. Finally, impact damage from various sources, such as hail or accidental collisions, can lead to dents, scratches, and holes. The cumulative effect of these factors significantly influences the lifespan and condition of the siding.
Cosmetic vs. Structural Damage
The distinction between cosmetic and structural damage is crucial for determining the appropriate repair strategy and prioritizing repairs. Cosmetic damage affects the appearance of the siding but doesn’t compromise its structural integrity. Scratches, minor dents, and fading are examples of cosmetic damage. These can often be repaired with relatively simple methods like repainting or minor touch-ups. In contrast, structural damage compromises the integrity of the siding, potentially leading to water infiltration or other problems.
Holes, deep dents, and significant corrosion are examples of structural damage, often requiring more extensive repairs, including panel replacement. Ignoring structural damage can lead to more significant and costly issues down the line.
Assessing Repair Needs
Before diving into the repair process, a thorough assessment of your aluminum siding is crucial. This step determines not only the extent of the damage but also the most cost-effective and practical solution – repair or replacement. A careful inspection will save you time, money, and potential headaches down the line. Remember, a small problem ignored can quickly escalate into a much larger, more expensive issue.
Proper assessment involves a systematic approach, combining visual inspection with careful consideration of the affected area’s size, location, and the overall condition of your siding. This will help you confidently decide whether a repair is feasible or if a full replacement is the better option. Let’s break down the process.
Visual Inspection of Aluminum Siding
A systematic visual inspection is the cornerstone of accurate damage assessment. Begin by examining the entire surface of your siding, paying close attention to areas prone to damage, such as corners, edges, and sections exposed to direct sunlight or harsh weather conditions. Look for dents, scratches, holes, discoloration, and signs of corrosion. Note the size and location of any damage.
For example, a small dent in an inconspicuous area might be easily repaired, while extensive corrosion covering a large section might necessitate replacement. A magnifying glass can be helpful for identifying minor imperfections.
Checklist for Assessing Aluminum Siding Damage
A structured checklist helps ensure you don’t overlook any crucial details during your inspection. Using a checklist promotes thoroughness and provides a documented record of the damage, useful when discussing repair options with contractors.
This checklist should include items such as:
- Overall Condition: Note the general condition of the siding. Is it mostly intact, or are there numerous areas of damage?
- Dents and Scratches: Document the number, size, and location of dents and scratches. Are they superficial or deep?
- Holes and Gaps: Identify any holes or gaps in the siding, noting their size and location. Are they caused by impact damage or deterioration?
- Corrosion: Check for signs of rust or corrosion. How extensive is the corrosion? Is it localized or widespread?
- Discoloration: Note any areas of discoloration, fading, or staining. Is this cosmetic or indicative of underlying damage?
- Loose or Damaged Panels: Examine each panel for looseness or damage to fasteners. Are panels loose, detached, or warped?
- Caulk and Sealant: Inspect the caulking and sealant around windows and doors. Is it cracked, deteriorated, or missing?
Repair vs. Replacement Scenarios
The decision to repair or replace aluminum siding depends on several factors. A cost-benefit analysis is often involved.
Examples illustrating when repair is preferable:
- Minor Dents and Scratches: Small dents and scratches, especially in less visible areas, can often be repaired using fillers and paint. This is a cost-effective solution compared to replacing entire panels.
- Localized Corrosion: If corrosion is limited to a small area, it might be possible to remove the affected section and replace it with a patch. This avoids the expense of replacing a whole panel.
- Loose Panels: Loose panels can often be re-secured using new fasteners. This is a relatively simple and inexpensive repair.
Examples where replacement is usually necessary:
- Extensive Corrosion: Widespread corrosion weakens the structural integrity of the siding, making repair impractical and potentially unsafe. Replacement ensures longevity and protects the underlying structure.
- Significant Damage: Large holes, deep gouges, or extensive damage to multiple panels usually necessitate replacement for aesthetic and structural reasons. Repairing such damage would be time-consuming and likely less effective.
- Outdated Siding: If the siding is old and showing significant wear and tear beyond simple repairs, replacement with modern, more energy-efficient siding might be a worthwhile investment.
Repair Methods and Techniques
Repairing aluminum siding successfully hinges on understanding the damage and employing the right techniques. Choosing the appropriate method—whether filling a small dent, patching a larger hole, or replacing a damaged panel entirely—directly impacts the longevity and aesthetic appeal of your home’s exterior. This section details the common approaches, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses to help you make informed decisions.Aluminum siding repair often involves a combination of techniques tailored to the specific damage.
The goal is to restore the siding’s structural integrity and its original appearance, seamlessly blending the repair with the surrounding panels. This is achieved through careful preparation, the selection of appropriate materials, and meticulous application.
Filling Dents
Minor dents, often caused by impacts from small objects, can usually be repaired without resorting to patching or panel replacement. A specialized epoxy putty, designed for exterior use and formulated to match the color of your siding, is ideal for this purpose. The putty’s flexibility allows it to conform to the shape of the dent and withstand the elements.
Applying a thin layer of primer before painting the repaired area ensures a seamless finish. Alternatively, a specialized aluminum dent puller may be used to carefully lift the dent from the inside. This may be more effective than putty for more significant dents, but is often not feasible without panel removal.
Patching Holes
Larger holes, resulting from impacts or deterioration, require a more substantial repair. Aluminum sheet metal, cut to the appropriate size and shape, offers a durable and long-lasting patch. The sheet metal can be secured using aluminum rivets or specialized exterior-grade adhesive, ensuring a secure and weatherproof seal. Matching the color of the existing siding to the patch requires careful paint matching or the use of pre-painted aluminum sheets.
Using a high-quality sealant around the edges of the patch prevents moisture intrusion and enhances the repair’s longevity.
Replacing Panels
Extensive damage or multiple small imperfections in a single panel often warrant replacement. This involves removing the damaged panel and installing a new one. This process necessitates careful removal of the old panel, paying close attention to not damaging adjacent panels or the underlying structure. The new panel should be securely fastened using appropriate fasteners, ensuring a tight fit and a visually appealing outcome.
If a complete panel replacement is necessary, matching the existing siding’s color and texture is crucial for maintaining the home’s aesthetic consistency. Consider sourcing replacement panels from the original manufacturer if possible for a precise match.
Patching Material Comparison: Epoxy Putty vs. Aluminum Sheet Metal
The choice between epoxy putty and aluminum sheet metal depends largely on the size and nature of the damage. Epoxy putty is best suited for small dents and minor imperfections, offering a relatively simple and quick repair. Aluminum sheet metal, on the other hand, is the preferred choice for larger holes and more significant damage, providing a robust and long-lasting solution.
| Feature | Epoxy Putty | Aluminum Sheet Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Suitable for | Small dents, minor scratches | Larger holes, significant damage |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Ease of Application | Easy | Moderate |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Siding Surface Preparation
Proper surface preparation is paramount for a successful repair. Failing to adequately prepare the surface can compromise the adhesion of the repair material, leading to premature failure. Careful attention to detail during this stage significantly improves the longevity and aesthetic appeal of the repair.
- Thoroughly clean the damaged area with a suitable detergent and water, removing any dirt, debris, or loose paint.
- Allow the area to dry completely before proceeding to the next step.
- If necessary, gently sand the area to create a smooth, even surface, ensuring a good bond with the repair material. Use fine-grit sandpaper to avoid further damaging the siding.
- Remove any loose or flaking paint around the damaged area to prevent peeling and ensure proper adhesion.
- Apply a suitable primer to the prepared surface, ensuring compatibility with both the siding and the repair material. This improves adhesion and creates a consistent surface for painting.
Tools and Materials
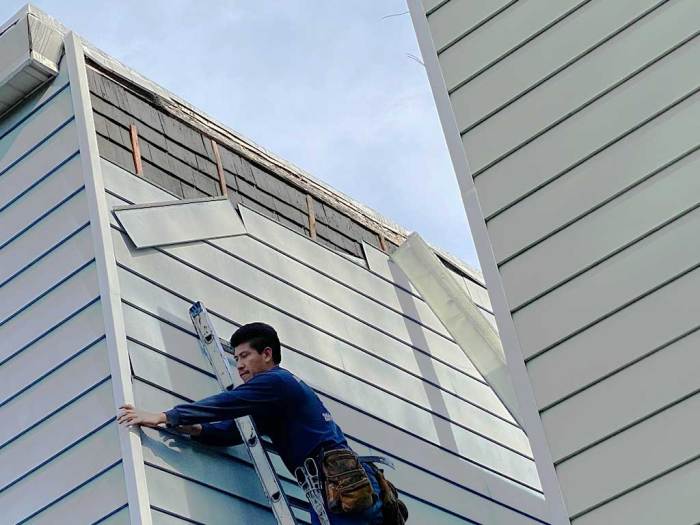

Successfully repairing aluminum siding hinges on having the right tools and materials at your disposal. The efficiency and quality of your repair will be directly impacted by your preparedness. Choosing the correct materials is crucial for a long-lasting, aesthetically pleasing result. Let’s dive into the specifics.
Proper preparation is key to a successful aluminum siding repair project. This includes gathering the necessary tools and materials, and understanding the safety precautions involved in handling them. Failing to do so could lead to inefficient work, potential injury, or even damage to your siding.
Essential Tools and Materials
The following list Artikels the essential tools and materials needed for most aluminum siding repair jobs. Remember that specific requirements may vary depending on the nature and extent of the damage.
- Measuring Tape: Accurate measurements are critical for cutting replacement panels to the correct size.
- Utility Knife or Tin Snips: Used for precise cutting of aluminum siding panels.
- Screwdrivers (Phillips and Flathead): Essential for removing and installing screws.
- Hammer: For gently tapping components into place (avoid excessive force).
- Putty Knife: Useful for removing old caulk and cleaning surfaces.
- Caulk Gun: For applying sealant around repaired areas to prevent water ingress.
- Aluminum Siding Repair Panels (Matching Color): The core material for replacement.
- Aluminum Siding Sealant/Caulk: A high-quality, weather-resistant sealant is vital for waterproofing.
- Safety Glasses: Always protect your eyes from flying debris.
- Work Gloves: Protect your hands from sharp edges and potential irritants.
Safety Precautions
Working with sharp tools and potentially hazardous materials necessitates a strong emphasis on safety. Neglecting safety precautions can lead to serious injuries. Always prioritize your safety and well-being.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses at all times to protect against flying debris from cutting or hammering.
- Hand Protection: Use work gloves to safeguard your hands from sharp edges and potential chemical irritants in sealants.
- Proper Ventilation: When working with sealants or paints, ensure adequate ventilation to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Sharp Tool Handling: Always handle sharp tools with care, keeping them away from exposed skin.
- Ladder Safety: If working at heights, use a sturdy ladder and follow all safety guidelines.
Material Selection
The type and severity of the damage will dictate the materials needed for the repair. Using inappropriate materials can compromise the repair’s longevity and aesthetic appeal. Matching existing siding is paramount.
For minor dents or scratches, a simple application of aluminum-specific touch-up paint may suffice. More extensive damage, such as holes or significant warping, will require replacement panels that match the existing siding in color, texture, and gauge (thickness). Always source replacement panels from a reputable supplier to ensure color consistency and quality.
When selecting sealant, opt for a high-quality, weather-resistant caulk specifically designed for exterior use and aluminum siding. Look for products with good adhesion properties and UV resistance to prevent cracking and deterioration over time. A failure to use appropriate sealant will leave your repair vulnerable to water damage, leading to future problems. For example, a cheap, low-quality sealant might fail within a year, requiring further repairs and additional costs.
Repairing Specific Damage Types: Aluminum Siding Repair
Addressing damage to your aluminum siding effectively requires a nuanced approach, tailored to the specific type of damage. Understanding the repair process for dents, holes, and discoloration will ensure a long-lasting and aesthetically pleasing result. This section details practical, step-by-step methods for tackling these common issues, empowering you to restore your siding to its former glory.
Dent Repair in Aluminum Siding, Aluminum Siding Repair
Removing dents from aluminum siding often involves carefully manipulating the metal back into its original shape. Minor dents can sometimes be coaxed out using gentle pressure from behind the siding, perhaps with a specialized tool like a suction cup dent puller or a carefully applied wooden block. For more stubborn dents, a combination of techniques might be necessary.
Learn about more about the process of Green Insulated Siding A Complete Guide in the field.
This could involve using a putty knife or similar tool to carefully work the metal from the back, while simultaneously supporting the area from the front to prevent further damage. After the dent is removed, any remaining imperfections can be filled using an aluminum-compatible filler and then carefully sanded smooth for a seamless finish. Remember, patience and a light touch are key to avoid creating more damage during the repair process.
Hole Repair in Aluminum Siding
Repairing holes in aluminum siding requires a more involved approach. The size and location of the hole will dictate the best repair method. Small holes can often be successfully patched using a piece of aluminum flashing or a specially formulated aluminum patching compound. This involves carefully cleaning the area around the hole, applying a suitable adhesive, and then pressing the patch firmly into place.
Once the adhesive has set, the patched area should be sealed with a high-quality exterior-grade sealant to prevent water ingress. Larger holes might necessitate cutting a larger section of siding to replace the damaged area completely, requiring more advanced skills and possibly the use of specialized tools like tin snips and rivets.
Addressing Discoloration or Fading
Discoloration or fading of aluminum siding is often caused by prolonged exposure to the elements, particularly ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. While you can’t reverse the damage completely, you can significantly improve the appearance. Cleaning the siding thoroughly with a suitable cleaning solution designed for aluminum siding is the first step. This will remove dirt, grime, and mildew that can contribute to discoloration.
After cleaning, consider applying a high-quality aluminum siding paint designed to protect against UV damage and restore color. Choose a paint specifically formulated for exterior use and ensure proper surface preparation before application for optimal results. Remember, regular cleaning and the application of protective coatings can help prevent future discoloration and extend the lifespan of your aluminum siding.
Cost Considerations
Repairing aluminum siding, whether you tackle it yourself or hire a pro, involves a financial commitment. Understanding the factors influencing the overall cost is crucial for budgeting and making informed decisions. This section will break down the cost components and offer strategies for minimizing expenses.The cost of aluminum siding repair is a multifaceted issue, influenced primarily by three key factors: labor costs, material expenses, and the severity of the damage.
Labor costs vary widely depending on your location, the contractor’s experience, and the complexity of the repair. Material costs depend on the type and quantity of aluminum siding needed, as well as any necessary fasteners, sealants, or primers. Finally, the extent of the damage—a small dent versus a large section needing replacement—significantly impacts the overall price. Let’s delve into each component in more detail.
Labor Costs
Labor costs represent a significant portion of the total repair bill. Highly skilled and experienced professionals command higher hourly rates compared to less experienced individuals. Geographical location also plays a role, with higher costs typically associated with areas with a higher cost of living and greater demand for skilled labor. For instance, a repair job in a bustling metropolitan area might cost significantly more than a similar job in a rural setting.
The complexity of the repair also affects labor costs; intricate repairs requiring specialized techniques or extensive time commitment naturally increase the overall cost. A simple dent repair will likely be cheaper than replacing a large section of damaged siding.
Material Costs
Material costs are dictated by the type and quantity of materials needed. Matching existing siding color and texture can sometimes be challenging, potentially increasing costs. The price of aluminum siding itself varies based on the manufacturer, quality, and thickness of the material. Additionally, any necessary supporting materials such as fasteners, sealants, and primers will add to the total cost.
High-quality, durable materials, while potentially more expensive upfront, often offer better long-term value and reduce the likelihood of future repairs. For example, using premium-grade sealant can prevent water damage and extend the life of the repair, ultimately saving money in the long run.
Extent of Damage
The extent of the damage is perhaps the most significant factor influencing repair costs. Minor damage, such as small dents or scratches, can often be repaired relatively inexpensively. However, extensive damage, including large holes, significant warping, or substantial sections requiring replacement, will drastically increase the overall cost. Consider a scenario where a single panel is damaged versus an entire wall section.
The difference in both materials and labor will be considerable. Accurate assessment of the damage is therefore crucial for obtaining accurate cost estimates.
DIY Repair versus Professional Repair
Choosing between DIY repair and hiring a professional involves weighing cost against expertise and time. DIY repair can potentially save money on labor costs, but it requires the necessary skills, tools, and time. Incorrect repairs can lead to further damage and increased costs down the line. Professional repair, while more expensive upfront, guarantees quality workmanship, potentially preventing future problems.
The cost difference can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the repair. For simple repairs, DIY might be a viable option. However, for complex jobs or extensive damage, hiring a professional is generally recommended to ensure the longevity and aesthetic appeal of your siding.
Saving Money on Aluminum Siding Repair
Several strategies can help reduce the overall cost of aluminum siding repair. Obtaining multiple quotes from different contractors allows for comparison and selection of the most competitive offer. Timing repairs strategically, for instance, during the off-season, may result in lower labor rates. Prioritizing repairs and addressing minor damage promptly can prevent escalation into more extensive and costly problems.
Finally, considering less expensive, yet still high-quality, materials can also help lower the overall cost. Careful planning and informed decision-making are key to minimizing expenses without compromising the quality of the repair.
Last Recap
Mastering aluminum siding repair isn’t just about fixing a cosmetic issue; it’s about extending the life of your home’s exterior and preserving its value. By understanding the causes of damage, employing the right techniques, and prioritizing preventative maintenance, you can ensure your aluminum siding remains a robust and attractive feature for years to come. Remember, a well-maintained exterior isn’t just aesthetically pleasing; it’s a smart investment in your home’s longevity and your peace of mind.
So, grab your tools, and let’s get started on transforming your siding!